/*****************************************************************
* Copyright (C) 2015 Intel Technology Co.,Ltd.*
******************************************************************
* lsitprocess.c
*
* DESCRIPTION:
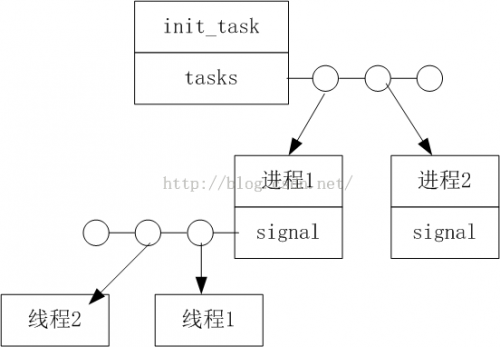
* 列出所有的进程/线程
* AUTHOR:
* 刘峰 11579502
*
* CREATED DATE:
* 2015年09月17日
* REVISION:
* 1.0
*
* MODIFICATION HISTORY
* --------------------
* $Log:$
* 刘峰 2015年09月17日 Creation
*****************************************************************/
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/err.h>
#include <linux/proc_fs.h>
#include <linux/time.h>
#include <linux/hrtimer.h>
#include <linux/kvm_para.h>
#include <linux/seq_file.h>
#include <asm/u
access.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <asm/msr.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <asm/page_64_types.h>
#include <linux/sched.h>
#define LOCAL static
#define KMOD_DBGDUMP(fmt, args...) printk(KERN_DEBUG "LISTPROCESS[%d] "fmt"
", __LINE__, args);
#define KMOD_RAWDUMP(args...) printk(args); /* RAW 信息输出 */
LOCAL struct proc_dir_entry *proc_file = NULL;
LOCAL int32_t kmod_action_sw = 8;
#define TEST_CASE_1 (1)
#define TEST_CASE_2 (2)
#define TEST_CASE_3 (3)
#define KMODSEPC
/******************************************************************************
* DESCRIPTION:
* 利用list_for_each_entry进行打印
* INPUTS:
* none
* OUTPUTS:
* none
* RETURNS:
* none
******************************************************************************/
void listprocess_test_case_1(void){
struct task_struct *task = NULL;
struct task_struct *p = NULL;
struct list_head *pos;
int count = 0;
printk("list_for_each
");
printk("PID COMM
");
task = &init_task;
list_for_each(pos, &task->tasks ) {
p = list_entry(pos, struct task_struct, tasks);
count++;
printk("%d %s
", p->pid, p->comm);
}
printk("Total process %d
", count);
return;
}
/******************************************************************************
* DESCRIPTION:
* 利用for_each_process进行打印
* INPUTS:
* none
* OUTPUTS:
* none
* RETURNS:
* none
******************************************************************************/
void listprocess_test_case_2(void){
struct task_struct *tsk;
int count = 0;
printk("for_each_process
");
printk("PID COMM
");
for_each_process(tsk){
count++;
printk("%d %s
", tsk->pid, tsk->comm);
}
printk("Total process %d
", count);
return;
}
/******************************************************************************
* DESCRIPTION:
* 利用for_each_process_thread进行打印
* INPUTS:
* none
* OUTPUTS:
* none
* RETURNS:
* none
******************************************************************************/
void listprocess_test_case_3(void){
struct task_struct *p;
struct task_struct *t;
int count = 0;
printk("for_each_process_thread
");
printk("PID COMM
");
for_each_process_thread(p,t){
count++;
printk("%d %s
", t->pid, t->comm);
}
printk("Total thread %d
", count);
return;
}
#if 1
KMODSEPC
#endif
/******************************************************************************
* DESCRIPTION:
* PROC 文件读方法
* INPUTS:
* none
* OUTPUTS:
* none
* RETURNS:
* none
******************************************************************************/
LOCAL int kmod_proc_read(struct seq_file * m, void * v)
{
seq_printf(m, "Entering kmod_proc_read
");
return 0;
}
/******************************************************************************
* DESCRIPTION:
* PROC 文件写方法
* INPUTS:
* none
* OUTPUTS:
* none
* RETURNS:
* none
******************************************************************************/
static ssize_t kmod_proc_write(struct file *file, const char __user *buffer, size_t count, loff_t *pos)
{
char debug_string[sizeof("4294967295")];
kmod_action_sw = 0;
KMOD_DBGDUMP("%s","Entering kmod_proc_write");
if (count >= sizeof(debug_string))
return -EINVAL;
if (copy_from_user(debug_string, buffer, count))
return -EFAULT;
debug_string[count] = '�';
if (sscanf(debug_string, "%d", &kmod_action_sw) != 1)
return -EINVAL;
KMOD_DBGDUMP("write kmod_action_sw = %d
", kmod_action_sw);
/*运行测试用例*/
switch(kmod_action_sw)
{
case TEST_CASE_1:
listprocess_test_case_1();
break;
case TEST_CASE_2:
listprocess_test_case_2();
break;
case TEST_CASE_3:
listprocess_test_case_3();
break;
default:
KMOD_DBGDUMP("%s","not support timer test case");
}
return count;
return count;
}
/******************************************************************************
* DESCRIPTION:
* PROC 文件打开方法
* INPUTS:
* none
* OUTPUTS:
* none
* RETURNS:
* none
******************************************************************************/
static int kmod_proc_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
return single_open(file, kmod_proc_read, NULL);
}
/*
* PROC文件操作列表
*/
LOCAL const struct file_operations kmod_proc_fops = {
.open = kmod_proc_open,
.read = seq_read,
.llseek = seq_lseek,
.release = seq_release,
.write = kmod_proc_write,
};
/******************************************************************************
* DESCRIPTION:
* 初始化PROC 目录
* INPUTS:
* none
* OUTPUTS:
* none
* RETURNS:
* none
******************************************************************************/
LOCAL int kmod_proc_init(void)
{
proc_file = proc_create("listprocess", 0666, NULL, &kmod_proc_fops);
if(!proc_file){
KMOD_DBGDUMP("%s","Can't create /proc/listprocess
");
}
KMOD_DBGDUMP("%s","kmod_proc_init OK
");
return 0;
}
/******************************************************************************
* DESCRIPTION:
* 删除PROC 目录
* INPUTS:
* none
* OUTPUTS:
* none
* RETURNS:
* none
******************************************************************************/
LOCAL void kmod_proc_remove(void)
{
remove_proc_entry("listprocess",NULL);
return;
}
/******************************************************************************
* DESCRIPTION:
* 模块初始化函数
* INPUTS:
* none
* OUTPUTS:
* none
* RETURNS:
* none
******************************************************************************/
LOCAL int32_t __init listprocess_init(void)
{
kmod_proc_init();
KMOD_DBGDUMP("%s","glistprocess_init init OK
");
return 0;
}
/******************************************************************************
* DESCRIPTION:
* 模块卸载函数
* INPUTS:
* none
* OUTPUTS:
* none
* RETURNS:
* none
******************************************************************************/
LOCAL void __exit listprocess_exit(void)
{
kmod_proc_remove();
KMOD_DBGDUMP("%s","listprocess_exit exit OK
");
return;
}
MODULE_LICENSE ( "GPL" );
module_init (listprocess_init);
module_exit (listprocess_exit);
.png)